C1 - Cx Synthetic Biology
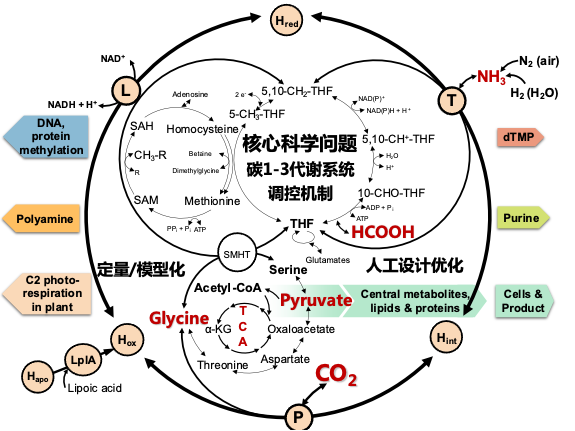
The regulation mechanisms and re-design of C1-Cx carbon metabolism network are the core scientific questions of this research. C1-Cx metabolism governs the most basic bioreactions for material and energy transformations and is nested in a complex network. We aim at a system-level understanding and re-design of it through quantification and modeling, and develop next-generation bioprocesses for synthesizing basic chemicals, amino acids, and future food (proteins) based on air (CO2, N2 ), water, and regenerative energy (light and electricity), contributing thus to carbon neutrality.
C1-Cx metabolism is also involved in many diseases, such as cancer and neurodegeneration. The quantitative and system-level study of C1-Cx metabolism is expected to provide new targets for their diagnosis and cure.
Selected literature
1. H. Zhang, Y. Li, J. Nie, J. Ren, AP Zeng (2020) Structure-based dynamic analyses of the glycine cleavage system suggests key residues for control of a key reaction step. Communications Biology. 3 (1), 1-12.
2. J Ren, W Wang, J Nie, W Yuan, AP Zeng (2022) Understanding and engineering glycine cleavage system and related metabolic pathways for C1-based biosynthesis. Adv. Biochem. Bioeng/Biotechnol., Springer.

